The Solow growth model suggests that countries with identical saving rates and population growth rates should converge to the same per capita income level.This result has been extended to include investment in human capital (education)as well as investment in physical capital.This hypothesis is referred to as the "conditional convergence hypothesis," since the convergence is dependent on countries obtaining the same values in the driving variables.To test the hypothesis,you collect data from the Penn World Tables on the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker (g6090)for the 1960-1990 sample period,and regress it on the (i)initial starting level of GD-P per worker relative to the United States in 1960 (RelProd60), (ii)average population growth rate of the country (n), (iii)average investment share of GDP from 1960 to 1990 (SK - remember investment equals savings),and (iv)educational attainment in years for 1985 (Educ).The results for close to 100 countries is as follows (numbers in parentheses are for heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors): 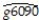 = 0.004 - 0.172 × n + 0.133 × SK + 0.002 × Educ - 0.044 × RelProd60,
= 0.004 - 0.172 × n + 0.133 × SK + 0.002 × Educ - 0.044 × RelProd60,
(0.007)(0.209)(0.015)(0.001)(0.008)
R2=0.537,SER = 0.011
(a)Is the coefficient on this variable significantly different from zero at the 5% level? At the 1% level?
(b)Test for the significance of the other slope coefficients.Should you use a one-sided alternative hypothesis or a two-sided test? Will the decision for one or the other influence the decision about the significance of the parameters? Should you always eliminate variables which carry insignificant coefficients?
Definitions:
Mate Choice Criteria
The qualities or characteristics individuals look for in potential breeding partners, influenced by evolutionary, social, and personal factors.
Financial Resources
Assets, capital, or funds that an individual or organization has available for spending or investment.
Passionate Love
A state of intense longing for union with another, characterized by the experience of excitement and fulfillment in the presence of a loved one, and distress during periods of separation.
Societally-Recognized
Societally-recognized refers to being acknowledged or validated by society or its major institutions, often related to roles, achievements, or statuses.
Q7: Though a cross hedge has somewhat higher
Q16: Large stock price moves reduce the effectiveness
Q29: Find the profit if the investor buys
Q31: A credit default swap is an ordinary
Q32: The class of linear conditionally unbiased estimators
Q35: One implication of the extended least squares
Q38: Find the profit if the investor enters
Q43: What is the probability of the following
Q51: To infer the political tendencies of the
Q56: You have estimated the following regression to