Using the 420 observations of the California School data set from your textbook,you estimate the following relationship: 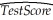 = 681.44 - 0.61LchPct
= 681.44 - 0.61LchPct
n=420,R2=0.75,SER=9.45
where TestScore is the test score and LchPct is the percent of students eligible for subsidized lunch (average = 44.7,max = 100,min = 0).
a.Interpret the regression result.
b.In your interpretation of the slope coefficient in (a)above,does it matter if you start your explanation with "for every x percent increase" rather than "for every x percentage point increase"?
c.The "overall" regression F-statistic is 1149.57.What are the degrees of freedom for this statistic?
d.Find the critical value of the F-statistic at the 1% significance level.Test the null hypothesis that the regression R2= 0.
e.The above equation was estimated using heteroskedasticity robust standard errors.What is the standard error for the slope coefficient?
Definitions:
Medication Adjustment
The process of changing the type, dosage, or frequency of medications based on a patient's health status.
Inhaler
A medical device used for delivering medication into the body via the lungs, often used for treating respiratory conditions such as asthma.
Puffs
Puffs generally refer to small, quick releases of air, smoke, vapor, or aerosolized substances, often used in the context of inhalation devices, like asthma inhalers, or in culinary terms to describe light, airy pastry products.
Refill Medication
The process of obtaining an additional supply of a prescription drug that has previously been dispensed.
Q9: If Xt and Yt are cointegrated,then the
Q10: The effect of decreasing the student-teacher ratio
Q19: The mean and variance of a Bernoille
Q34: The central limit theorem<br>A)states conditions under which
Q38: A risk of equity swaps is that
Q39: Consider the simple regression model Yi =
Q48: Imagine that you were told that the
Q49: The lag length in a VAR using
Q49: In order to calculate the regression R2
Q55: To decide whether the slope coefficient indicates