Females,on average,are shorter and weigh less than males.One of your friends,who is a pre-med student,tells you that in addition,females will weigh less for a given height.To test this hypothesis,you collect height and weight of 29 female and 81 male students at your university.A regression of the weight on a constant,height,and a binary variable,which takes a value of one for females and is zero otherwise,yields the following result: 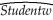 = -229.21 - 6.36 × Female + 5.58 × Height,R2=0.50,SER = 20.99
= -229.21 - 6.36 × Female + 5.58 × Height,R2=0.50,SER = 20.99
(43.39)(5.74)(0.62)
where Studentw is weight measured in pounds and Height is measured in inches (heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors in parentheses).
Calculate t-statistics and carry out the hypothesis test that females weigh the same as males,on average,for a given height,using a 10% significance level.What is the alternative hypothesis? What is the p-value? What critical value did you use?
Definitions:
Dimensioning
The practice of specifying part sizes, shapes, and features on technical drawings or CAD models, including dimensions, tolerances, and other critical specifications.
Two-Axis
Referring to systems, machines, or components that operate or move in two different directions or planes, typically described by x and y coordinates.
Negative Y Values
Represent values below the horizontal axis in a Cartesian coordinate system, typically indicating a decrease or loss.
Accurately Positioning
The precise placement or alignment of components in relation to each other or to a reference point, crucial for the correct functioning of mechanical systems.
Q9: Discuss the properties of the OLS estimator
Q9: Swaps obligate delivery of either bonds or
Q13: A diff swap pays off in one
Q24: Two random variables X and Y are
Q31: Math and verbal SAT scores are each
Q38: In which one of the following types
Q39: In estimating the original relationship between money
Q43: Based on the price sensitivity hedge ratio,if
Q43: What is the probability of the following
Q55: Eurodollar futures are widely used to hedge