You recall from one of your earlier lectures in macroeconomics that the per capita income depends on the savings rate of the country: those who save more end up with a higher standard of living.To test this theory,you collect data from the Penn World Tables on GDP per worker relative to the United States (RelProd)in 1990 and the average investment share of GDP from 1980-1990 (SK),remembering that investment equals saving.The regression results in the following output: 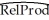 = -0.08 + 2.44×SK,R2=0.46,SER = 0.21
= -0.08 + 2.44×SK,R2=0.46,SER = 0.21
(0.04)(0.38)
(a)Interpret the regression results carefully.
(b)Calculate the t-statistics to determine whether the two coefficients are significantly different from zero.Justify the use of a one-sided or two-sided test.
(c)You accidentally forget to use the heteroskedasticity-robust standard errors option in your regression package and estimate the equation using homoskedasticity-only standard errors.This changes the results as follows: 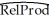 = -0.08 + 2.44×SK,R2=0.46,SER = 0.21
= -0.08 + 2.44×SK,R2=0.46,SER = 0.21
(0.04)(0.26)
You are delighted to find that the coefficients have not changed at all and that your results have become even more significant.Why haven't the coefficients changed? Are the results really more significant? Explain.
(d)Upon reflection you think about the advantages of OLS with and without homoskedasticity-only standard errors.What are these advantages? Is it likely that the error terms would be heteroskedastic in this situation?
Definitions:
Therapeutic Drug Dose
This refers to the calculated amount of a medication prescribed for intake or administration to achieve a desired therapeutic effect.
Visual Hallucinations
A form of hallucination involving seeing things that are not present or do not exist.
Tachycardia
A condition characterized by an abnormally fast heart rate, typically over 100 beats per minute in adults.
Hypertension
A chronic medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated.
Q4: In Chapter 10 of your textbook,panel data
Q18: An interest rate payer swaption is more
Q22: In the real-world,financial decisions are irrelevant,so there
Q24: Two random variables X and Y are
Q27: Interest rate swap volume is greater than
Q36: A hedge of a specific stock's price
Q37: Assume that Y is normally distributed N(μ,σ2).Moving
Q53: At the Stock and Watson (http://www.pearsonhighered.com/stock_watson)website,go to
Q56: The following OLS assumption is most likely
Q64: Using the 420 observations of the California