The neoclassical growth model predicts that for identical savings rates and population growth rates,countries should converge to the per capita income level.This is referred to as the convergence hypothesis.One way to test for the presence of convergence is to compare the growth rates over time to the initial starting level,i.e. ,to run the regression 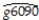 =
= 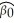 +
+ 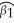 × RelProd60 ,where g6090 is the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker for the 1960-1990 sample period,and RelProd60 is GDP per worker relative to the United States in 1960.Under the null hypothesis of no convergence,β1 = 0;H1 : β1 < 0,implying ("beta")convergence.Using a standard regression package,you get the following output:
× RelProd60 ,where g6090 is the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker for the 1960-1990 sample period,and RelProd60 is GDP per worker relative to the United States in 1960.Under the null hypothesis of no convergence,β1 = 0;H1 : β1 < 0,implying ("beta")convergence.Using a standard regression package,you get the following output:
Dependent Variable: G6090
Method: Least Squares
Date: 07/11/06 Time: 05:46
Sample: 1 104
Included observations: 104
White Heteroskedasticity-Consistent Standard Errors & Covariance 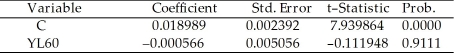
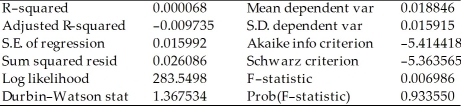 You are delighted to see that this program has already calculated p-values for you.However,a peer of yours points out that the correct p-value should be 0.4562.Who is right?
You are delighted to see that this program has already calculated p-values for you.However,a peer of yours points out that the correct p-value should be 0.4562.Who is right?
Definitions:
Studied Hard
A phrase indicating the process of dedicating significant effort and time to learning or mastering a subject matter.
Poorly
In an unsatisfactory, inadequate, or unsuccessful manner, often describing performance or condition.
First Information
The initial data or facts received about a situation, topic, or phenomenon, which can significantly influence perceptions and decisions.
Time Pressure
The stress or urgency of completing tasks or making decisions within a limited time frame.
Q2: The absence of a daily settlement is
Q10: Prove that under the extended least squares
Q14: Which of the following correctly expresses the
Q17: To choose the number of lags in
Q18: An interest rate payer swaption is more
Q24: A scatterplot<br>A)shows how Y and X are
Q31: With heteroskedastic errors,the weighted least squares estimator
Q37: A seller of a put option on
Q38: Using the model Y = Xβ +
Q64: You have read about the so-called catch-up