In a Monte Carlo study,econometricians generate multiple sample regression functions from a known population regression function.For example,the population regression function could be Yi = β0 + β1Xi = 100 - 0.5 Xi.The Xs could be generated randomly or,for simplicity,be nonrandom ("fixed over repeated samples").If we had ten of these Xs,say,and generated twenty Ys,we would obviously always have all observations on a straight line,and the least squares formulae would always return values of 100 and 0.5 numerically.However,if we added an error term,where the errors would be drawn randomly from a normal distribution,say,then the OLS formulae would give us estimates that differed from the population regression function values.Assume you did just that and recorded the values for the slope and the intercept.Then you did the same experiment again (each one of these is called a "replication").And so forth.After 1,000 replications,you plot the 1,000 intercepts and slopes,and list their summary statistics.
Sample: 1 1000
BETA0_HAT BETA1_HAT
Mean 100.014 -0.500
Median 100.021 -0.500
Maximum 106.348 -0.468
Minimum 93.862 -0.538
Std.Dev.1.994 0.011
Skewness 0.013 -0.042
Kurtosis 3.026 2.986
Jarque-Bera 0.055 0.305
Probability 0.973 0.858
Sum 100014.353 -499.857
Sum Sq.Dev.3972.403 0.118
Observations 1000.000 1000.000
Here are the corresponding graphs: 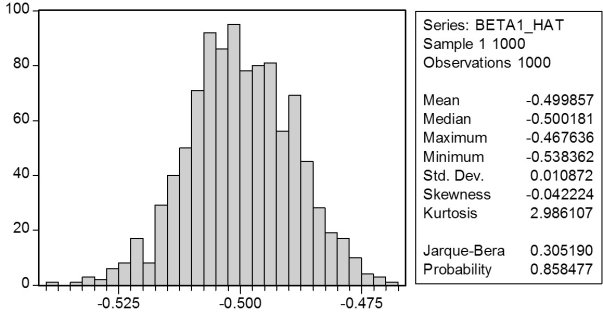
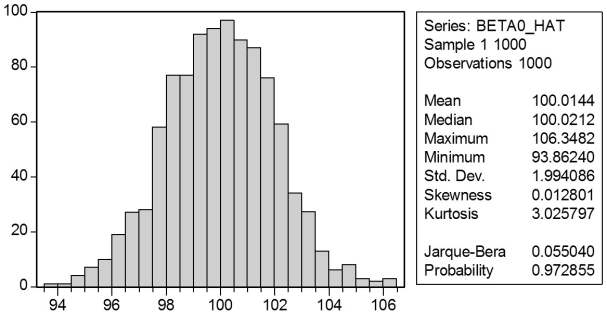 Using the means listed next to the graphs,you see that the averages are not exactly 100 and -0.5.However,they are "close." Test for the difference of these averages from the population values to be statistically significant.
Using the means listed next to the graphs,you see that the averages are not exactly 100 and -0.5.However,they are "close." Test for the difference of these averages from the population values to be statistically significant.
Definitions:
Dissociative Identity Disorder
A psychological disorder marked by the presence of two or more distinct personality states or identities.
New Identity
The adoption or development of a new personal or group identity, often differing substantially from one previously held.
Cultural Differences
Cultural differences refer to the diversity of customs, beliefs, arts, life ways, and social practices among people from different backgrounds.
DSM-5
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 5th Edition, a standardized classification of mental disorders used by mental health professionals in the U.S.
Q11: Consider the multiple regression model from Chapter
Q14: A professor in your microeconomics lectures derived
Q16: When the sample size n is large,the
Q17: Minimization of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2833/.jpg" alt="Minimization of
Q18: (Requires Appendix material)This question requires you to
Q37: A currency swap without the exchange of
Q41: When Xt is strictly exogenous,the following estimator(s)of
Q52: Use a standard spreadsheet program,such as Excel,to
Q58: At a mathematical level,if the two conditions
Q62: You have collected data from Major League