The neoclassical growth model predicts that for identical savings rates and population growth rates,countries should converge to the per capita income level.This is referred to as the convergence hypothesis.One way to test for the presence of convergence is to compare the growth rates over time to the initial starting level.
(a)If you regressed the average growth rate over a time period (1960-1990)on the initial level of per capita income,what would the sign of the slope have to be to indicate this type of convergence? Explain.Would this result confirm or reject the prediction of the neoclassical growth model?
(b)The results of the regression for 104 countries were as follows: 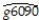 = 0.019 - 0.0006 × RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.00007,SER = 0.016,
= 0.019 - 0.0006 × RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.00007,SER = 0.016,
where g6090 is the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker for the 1960-1990 sample period,and RelProd60 is GDP per worker relative to the United States in 1960.
Interpret the results.Is there any evidence of unconditional convergence between the countries of the world? Is this result surprising? What other concept could you think about to test for convergence between countries?
(c)You decide to restrict yourself to the 24 OECD countries in the sample.This changes your regression output as follows: 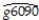 = 0.048 - 0.0404 RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.82 ,SER = 0.0046
= 0.048 - 0.0404 RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.82 ,SER = 0.0046
How does this result affect your conclusions from above?
Definitions:
Change-Of-Shift Report
A communication tool used by healthcare providers to transfer patient care information during transitions between shifts.
Nasal Cannula
A device used to deliver supplemental oxygen or increased airflow to a patient in need, consisting of a lightweight tube which on one end splits into two prongs that are placed in the nostrils.
Self-Administer Insulin
The process by which individuals with diabetes inject insulin themselves to manage blood glucose levels.
Teaching Successful
The act or practice of imparting knowledge or skills in a way that leads to the learners' understanding and application of the material, resulting in achieving desired learning outcomes.
Q6: The long-run cumulative dynamic multiplier<br>A)cannot be calculated
Q7: Negative autocorrelation in the change of a
Q14: All of the following are reasons for
Q16: You have decided to analyze the year-to-year
Q16: When there is a single instrument and
Q19: Using the California School data set from
Q27: When testing joint hypothesis,you should<br>A)use t-statistics for
Q29: Females,on average,are shorter and weigh less than
Q30: A multiperiod regression forecast h periods into
Q47: A seasonal binary (or indicator or dummy)variable,in