The neoclassical growth model predicts that for identical savings rates and population growth rates,countries should converge to the per capita income level.This is referred to as the convergence hypothesis.One way to test for the presence of convergence is to compare the growth rates over time to the initial starting level.
(a)If you regressed the average growth rate over a time period (1960-1990)on the initial level of per capita income,what would the sign of the slope have to be to indicate this type of convergence? Explain.Would this result confirm or reject the prediction of the neoclassical growth model?
(b)The results of the regression for 104 countries were as follows: 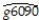 = 0.019 - 0.0006 × RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.00007,SER = 0.016,
= 0.019 - 0.0006 × RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.00007,SER = 0.016,
where g6090 is the average annual growth rate of GDP per worker for the 1960-1990 sample period,and RelProd60 is GDP per worker relative to the United States in 1960.
Interpret the results.Is there any evidence of unconditional convergence between the countries of the world? Is this result surprising? What other concept could you think about to test for convergence between countries?
(c)You decide to restrict yourself to the 24 OECD countries in the sample.This changes your regression output as follows: 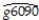 = 0.048 - 0.0404 RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.82 ,SER = 0.0046
= 0.048 - 0.0404 RelProd60 ,R2 = 0.82 ,SER = 0.0046
How does this result affect your conclusions from above?
Definitions:
Financing Activities
Transactions related to raising capital and repaying investors, included within the cash flow statement.
Creditors
Individuals or institutions that lend money or extend credit, and to whom an entity owes money.
Long-Term Debt
Financial obligations of a business or an individual that are due more than one year in the future.
Statement Of Cash Flows
A financial statement showing the inflows and outflows of cash and cash equivalents over a specific period, categorizing them into operating, investing, and financing activities.
Q3: To analyze the situation of simultaneous causality
Q4: A forward contract has which of the
Q9: You have read the analysis in chapter
Q11: You have collected data for 104 countries
Q29: IQ scores are normally distributed with an
Q41: When Xt is strictly exogenous,the following estimator(s)of
Q42: An estimator <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2833/.jpg" alt="An estimator
Q52: Use a standard spreadsheet program,such as Excel,to
Q58: The interpretation of the slope coefficient in
Q60: To calculate the homoskedasticity-only overall regression F-statistic,you