Define the GLS estimator and discuss its properties when Ω is known.Why is this estimator sometimes called infeasible GLS? What happens when Ω is unknown? What would the Ω matrix look like for the case of independent sampling with heteroskedastic errors,where var(ui  Xi)= ch(Xi)= σ2
Xi)= ch(Xi)= σ2 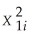 ? Since the inverse of the error variance-covariance matrix is needed to compute the GLS estimator,find Ω-1.The textbook shows that the original model Y = Xβ + U will be transformed into
? Since the inverse of the error variance-covariance matrix is needed to compute the GLS estimator,find Ω-1.The textbook shows that the original model Y = Xβ + U will be transformed into 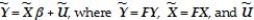 = FU,and
= FU,and 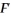 F = Ω-1.Find F in the above case,and describe what effect the transformation has on the original data.
F = Ω-1.Find F in the above case,and describe what effect the transformation has on the original data.
Definitions:
Budgeted Capacity
The amount of production or activity level planned for a future period, based on budget allocations.
Practical Capacity
The maximum amount of work or output that can be realistically achieved in a specific period under normal operating conditions.
Cost Allocation
The process of assigning indirect costs to different departments, products, or projects based on relevant distribution bases.
Cost Pool
A grouping of individual costs, typically by department or service center, from which cost allocations are made.
Q18: The net weight of a bag of
Q26: The OLS estimator<br>A)has the multivariate normal asymptotic
Q41: Below you are asked to decide on
Q42: In a simple regression with an intercept
Q43: Being a competitive female swimmer,you wonder if
Q46: Experimental data are often<br>A)observational data.<br>B)binary data,in that
Q48: The sample regression line estimated by OLS<br>A)has
Q49: A nonlinear function<br>A)makes little sense,because variables in
Q65: In a multiple regression framework,the slope coefficient
Q119: The sum of the column percents in