Define the GLS estimator and discuss its properties when Ω is known.Why is this estimator sometimes called infeasible GLS? What happens when Ω is unknown? What would the Ω matrix look like for the case of independent sampling with heteroskedastic errors,where var(ui  Xi)= ch(Xi)= σ2
Xi)= ch(Xi)= σ2 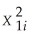 ? Since the inverse of the error variance-covariance matrix is needed to compute the GLS estimator,find Ω-1.The textbook shows that the original model Y = Xβ + U will be transformed into
? Since the inverse of the error variance-covariance matrix is needed to compute the GLS estimator,find Ω-1.The textbook shows that the original model Y = Xβ + U will be transformed into 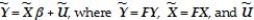 = FU,and
= FU,and 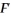 F = Ω-1.Find F in the above case,and describe what effect the transformation has on the original data.
F = Ω-1.Find F in the above case,and describe what effect the transformation has on the original data.
Definitions:
Tuscan Poet
Refers to Dante Alighieri, the renowned Italian poet of the Late Middle Ages, known for his masterpiece, "The Divine Comedy."
Classical Architecture
An architectural style influenced by the buildings of ancient Greece and Rome, characterized by symmetry, columns, and elaborate decoration.
Flying Buttresses
Architectural features consisting of external supports that transfer the thrust of a vault or roof to support piers, critical in the construction of Gothic cathedrals.
Pointed Arches
Architectural elements with pointed tops, characteristic of Gothic architecture, that allow for taller and more slender structures.
Q2: A study investigated the impact of house
Q6: You have collected data on individuals and
Q26: The probit model<br>A)is the same as the
Q35: One implication of the extended least squares
Q35: A binary variable is often called a<br>A)dummy
Q39: In estimating the original relationship between money
Q47: You should use the QLR test for
Q61: (Requires Statistics background beyond Chapters 2 and
Q62: Using a spreadsheet program such as Excel,plot
Q96: The chi-square distribution is _.<br>A)skewed to the