Consider the following model of demand and supply of coffee:
Demand: 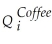 = β1
= β1 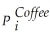 + β2
+ β2 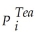 + ui
+ ui
Supply: 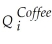 = β3
= β3 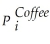 + β4
+ β4 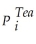 + β5Weather + vi
+ β5Weather + vi
(variables are measure in deviations from means,so that the constant is omitted).
What are the expected signs of the various coefficients this model? Assume that the price of tea and Weather are exogenous variables.Are the coefficients in the supply equation identified? Are the coefficients in the demand equation identified? Are they overidentified? Is this result surprising given that there are more exogenous regressors in the second equation?
Definitions:
SSR
Stands for Sum of Squares due to Regression, which quantifies the variation explained by the regression model, comparing the estimated values to the mean of the dependent variable.
SST
Total sum of squares in statistical analysis, representing the total variation in the observed data relative to the mean.
Multiple Linear Regression
A statistical technique that models the relationship between a dependent variable and two or more independent variables by fitting a linear equation to observed data.
Partial Regression Slope Coefficients
Quantitative measures in multiple regression models that represent the rate of change in the dependent variable for one-unit change in the predictor variable, holding other variables constant.
Q2: Let n<sub>1</sub> represent the sample size of
Q3: The Bayes-Schwarz Information Criterion (BIC)is given by
Q5: The accompanying graph <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2833/.jpg" alt="The accompanying
Q5: Finite-sample distributions of the OLS estimator and
Q15: The power of the test is<br>A)dependent on
Q17: All of the following are good reasons
Q29: Consider a panel regression of unemployment rates
Q38: A study was done to determine if
Q46: Earnings functions,whereby the log of earnings is
Q54: The pooled two-sample t procedure can be