In this experiment,the risk-taking propensity of 90 inner city drug users was measured using a repeated measures test called the Behavioral Analogue Risk Task (BART;Lejuez et al. ,2002) .The higher the BART score,the higher the risk-taking propensity.Participants also filled out questionnaires so that their Psychopathic Personality Inventory (PPI) scores could be computed.PPI scores are used to detect psychopathic traits in a covert manner and are a common indicator of one's level of psychopathy.The main goal of the experiment was to examine the relationship between risk-taking (measured by BART) based on one's level of psychopathy (measured by PPI on a scale of 0-100) ,gender (1 for male and 2 for female) ,and heroin use (1 for heroin use and 0 for no heroin use) .Below is a partial output of a multiple regression analysis. 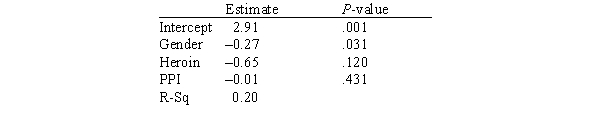 What proportion of the variation of the response variable is explained by the explanatory variables?
What proportion of the variation of the response variable is explained by the explanatory variables?
Definitions:
Capacity To Acquire
The ability to learn or gain new skills, knowledge, or abilities, often considered in the context of individual or organizational growth and development.
Arouse Controversy
To provoke public debate or dispute, often by challenging established norms or opinions.
Interested
Exhibiting curiosity or concern about something or someone, showing a desire to be involved with or learn more about the object of interest.
Perfectly Rational
A theoretical state in decision-making where an individual makes decisions that lead to the optimal outcome, based entirely on logical reasoning.
Q7: The data referred to in this question
Q11: A researcher wished to compare the effect
Q20: A study was undertaken to assess the
Q33: Intrinsic reinforcers<br>A)bribe a person to engage in
Q44: It is widely believed that a person's
Q55: According to John B.Watson,the founder of American
Q74: Training a rat to push a lever
Q82: During the early part of the 1994
Q91: B.F.Skinner theorized that<br>A)children would develop better if
Q144: Shaping is achieved through<br>A)discrimination training.<br>B)generalization.<br>C)higher-order conditioning.<br>D)successive approximations.