In this experiment,the risk-taking propensity of 90 inner city drug users was measured using a repeated measures test called the Behavioral Analogue Risk Task (BART;Lejuez et al. ,2002) .The higher the BART score,the higher the risk-taking propensity.Participants also filled out questionnaires so that their Psychopathic Personality Inventory (PPI) scores could be computed.PPI scores are used to detect psychopathic traits in a covert manner and are a common indicator of one's level of psychopathy.The main goal of the experiment was to examine the relationship between risk-taking (measured by BART) based on one's level of psychopathy (measured by PPI on a scale of 0-100) ,gender (1 for male and 2 for female) ,and heroin use (1 for heroin use and 0 for no heroin use) .Below is a partial output of a multiple regression analysis. 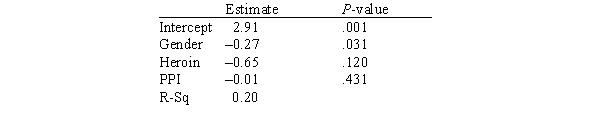 Based on this model,are men bigger risktakers than women?
Based on this model,are men bigger risktakers than women?
Definitions:
Dominant
Possessing authority, control, or influence over others, often in a social, genetic, or interactional context.
Dizygotic Twins
Also known as fraternal twins, they develop from two different eggs fertilized by two different sperm, resulting in genetically unique siblings born at the same time.
Monozygotic Twins
Also known as identical twins, these are siblings who originate from the same fertilized egg, sharing nearly 100% of their genetic material.
X-Linked Disorders
Genetic conditions caused by mutations in genes on the X chromosome, often affecting males more severely than females.
Q14: Some researchers have conjectured that stem-pitting disease
Q27: A researcher is investigating possible explanations for
Q30: The Consumers Union measured the gas mileage
Q47: Researchers at a car resale company are
Q51: Edward Tolman and his colleague,C.H.Honzik,noted that _
Q55: What condition is necessary for a process
Q60: What proportion of the variation in the
Q83: The bar graph below represents the highest
Q144: Shaping is achieved through<br>A)discrimination training.<br>B)generalization.<br>C)higher-order conditioning.<br>D)successive approximations.
Q201: Behaviorists focus on a basic kind of