Consider the Following Linear Programming Problem Use the Two Tables Below to Create the Initial Tableau
Consider the following linear programming problem:
Use the two tables below to create the initial tableau and perform 1 pivot. 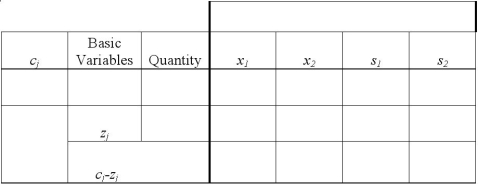
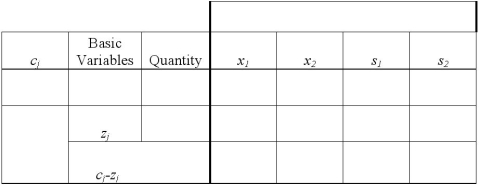
Definitions:
Uncollectible Accounts
Financial accounts receivable that are deemed unlikely to be collected, leading to their categorization as bad debts.
Year-end Adjustment
Adjustments made to the books of accounts at the end of a fiscal year to reflect accurate financial information.
Uncollectible Account
Accounts receivable that cannot be collected from customers, often considered as bad debt.
Small Regular Payments
Recurring payments made on a consistent basis, often referring to installments or subscriptions of manageable amounts.
Q4: What is the utilization rate for the
Q5: The branch and bound method of solving
Q16: When solving a linear programming problem, a
Q40: Choose one criminal who you are familiar
Q63: If the daily demand is 25 and
Q78: How much time will be used?
Q78: Compared to other academic disciplines, criminal justice
Q79: If the number of unique assignments is
Q91: Determine the optimal shortage level.
Q129: A trend is a gradual, long-term, up-or-down