Suppose you wish to test the null hypothesis that three binomial parameters 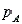 ,
, 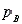 , and
, and 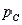 are equal versus the alternative hypothesis that at least two of the parameters differ. Independent random samples of 100 observations were selected from each of the populations. The data are shown in the table:
are equal versus the alternative hypothesis that at least two of the parameters differ. Independent random samples of 100 observations were selected from each of the populations. The data are shown in the table: 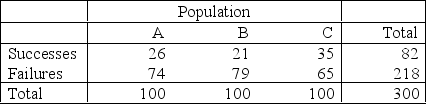
a. Write the null and alternative hypotheses for testing the equality of the three binomial proportions.
b. Calculate the test statistic and find the approximate p-value for the test in the previous question.
c. Use the approximate p-value to determine the statistical significance of your results. If the results are statistically significant, explore the nature of the differences in the three binomial proportions.
Definitions:
Acquisition
In learning theory, the process by which a new behavior is learned or a new association is formed, often discussed in the context of classical and operant conditioning.
Classical Conditioning
A learning process that occurs through associations between an environmental stimulus and a naturally occurring stimulus.
Extinction
The process by which a species, genus, or family of organisms becomes extinct, no longer existing and living in the world.
Spontaneous Recovery
The rebirth of an extinguished response after a break, without the need for relearning.
Q14: In a multiple regression analysis, the regression
Q16: In publishing the results of some research
Q28: To apply the Wilcoxon rank sum test
Q37: Refer to Attitude Test Narrative. State the
Q67: Nonparametric tests are methods of inference that
Q83: Historically, a bank has employed 50%
Q86: In a regression setting, you should select
Q92: In a multiple regression model, if there
Q112: In a Wilcoxon signed-rank test for matched
Q128: Refer to Ice Cream Sales Narrative. Find