UBC Building Signs Narrative
A researcher at University of British Columbia (UBC) wanted to determine whether different building signs (building maps versus wall signage) affect the total amount of time visitors require to reach their destination and whether that time depends on whether the starting location is inside or outside the building. Three subjects were assigned to each of the combinations of signs and starting locations, and travel time in seconds from beginning to destination was recorded. A partial computer output of the appropriate analysis is given below:
ANOVA Table 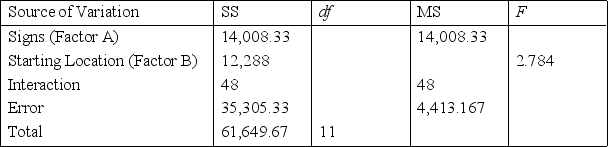
-Refer to UBC Building Signs Narrative. In order to determine the critical value of the F ratio against which to test for differences between the levels of factor B, which numerator and which denominator, respectively, for df should we use?
Definitions:
Cerebral Cortex
The outermost layer of the brain, involved in high-level functions such as thought, language, memory, and consciousness.
Hearing
The sense by which sound is perceived, involving the detection of vibrations and changes in pressure in the ear.
Sensory Systems
The parts of the nervous system that are involved in receiving and processing sensory information from the environment.
Primary Somatosensory Cortex
The primary somatosensory cortex is a region in the brain that processes tactile information, including sensations of touch, pressure, pain, and temperature.
Q28: Which of the following is the appropriate
Q30: In testing <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4962/.jpg" alt="In testing
Q40: Refer to Average Battery Life Narrative. Compute
Q68: In a two-way factor ANOVA, the total
Q90: In the simple linear regression model, what
Q97: The randomized block design is a two-way
Q111: A travel agency primarily reserves flights
Q133: In a two-way ANOVA, there are 4
Q142: Refer to Young Aspen Trees and Growth
Q173: In making inferences about a population mean