Two independent samples are selected at random from two normal populations. The sample statistics are as follows: 
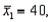
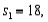

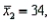 and
and 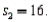 Assuming that a two-tailed hypothesis test is conducted at α = 0.05, what is the critical value?
Assuming that a two-tailed hypothesis test is conducted at α = 0.05, what is the critical value?
Definitions:
Wired Ethernet Networks
Networks that use physical cables, such as copper or fiber optics, to connect devices and facilitate high-speed data transmission.
Encryption
Turning information or data into a secret code to prevent it from being accessed by those without permission.
Cellular Network
A communication network where the last link is wireless, often used for mobile phone communication, it's structured into cells, each served by a fixed-location transceiver.
Internet Access
The ability of individuals and organizations to connect to the Internet using computer terminals, computers, and other devices; and to access services such as email and the World Wide Web.
Q7: When the actual values y of a
Q10: In the randomized block design for ANOVA
Q26: In testing <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4962/.jpg" alt="In testing
Q51: In a one-way ANOVA, if <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4962/.jpg"
Q64: Refer to Healthy Dog Food Narrative. What
Q76: For a t distribution with 12 degrees
Q77: Refer to Environment Canada Project Narrative.
Q83: Refer to Tennis Magazine Narrative. Calculate the
Q124: Refer to Healthy Dog Food Narrative. Set
Q138: A 95% confidence interval for the population