In testing 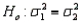 vs.
vs. 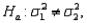 the larger the sample sizes from the two populations, the smaller will be the chance of committing a Type I error.
the larger the sample sizes from the two populations, the smaller will be the chance of committing a Type I error.
Definitions:
Permanent Hearing Loss
A lasting inability to hear partially or completely in one or both ears, which can result from genetic factors, aging, exposure to loud noise, or certain diseases.
Basilar Membrane
A membrane in the cochlea of the inner ear that vibrates in response to sound and plays a key role in the sense of hearing.
Auditory Information
Data or knowledge received and processed through the sense of hearing.
Trigeminal Nerve
The fifth cranial nerve responsible for sensory data such as tactition (pressure), thermoception (temperature), and nociception (pain) from the face and head; it also manages motor functions such as biting and chewing.
Q3: The p-value for a hypothesis test is
Q15: Refer to Defective Toasters Narrative. Describe the
Q52: In order to estimate the average number
Q71: The statistic <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4962/.jpg" alt="The statistic
Q74: Refer to Running Shoes Narrative. What are
Q103: What is the type of sample statistic
Q107: When we test for differences between the
Q128: In a hypothesis test, if the null
Q130: As the significance level <span
Q136: Assume that two independent random samples of