Population Samples Narrative
A sample is selected from one of two populations, 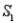 and
and 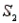 , with probabilities P(
, with probabilities P( 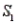 ) = 0.80 and P(
) = 0.80 and P( 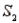 ) = 0.20. If the sample has been selected from
) = 0.20. If the sample has been selected from 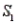 , the probability of observing an event A is P(A/
, the probability of observing an event A is P(A/ 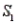 ) = 0.15. Similarly, If the sample has been selected from
) = 0.15. Similarly, If the sample has been selected from 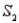 , the probability of observing A is P(A/
, the probability of observing A is P(A/ 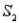 ) = 0.25.
) = 0.25.
-Refer to Population Samples Narrative. If a sample is randomly selected and event A is observed, what is the probability that the sample was selected from population 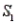 ? From population
? From population 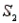 ?
?
Definitions:
Loanable Funds
The supply of available capital in the financial markets for borrowing, which can be used for investment purposes by individuals and businesses.
Future Consumption
The use of goods or services at a later date, often facilitated by saving or investing in the present.
Productivity of Capital Goods
The effectiveness with which capital goods, such as machinery and equipment, produce goods or services.
Loanable Funds
The money available for borrowing in the financial market, originating from people or entities who save some part of their income.
Q1: When all the numbers in the data
Q27: Refer to Drug Offenders Narrative. Find the
Q76: Suppose the records of a motel show
Q80: Members of the normal probability distribution family
Q81: Refer to Number of Cars Narrative. Find
Q95: All the outcomes contained in one or
Q128: Refer to Scholarship Narrative. What is the
Q133: Refer to College Applicants Narrative. If applicants
Q154: For a continuous random variable x and
Q196: The standard deviation is expressed in terms