(Scenario: Payoff Matrix for Airbus and Boeing) This payoff matrix describes actions in developing so-called superjumbo jets that can carry 600 or more passengers. In each element, the lower-left value gives the outcome for Boeing based on the action of Airbus and the upper-right value gives the outcome for Airbus based on the action of Boeing. For example, in element A, each company will lose $10 million if they both decide to produce superjumbo jets. 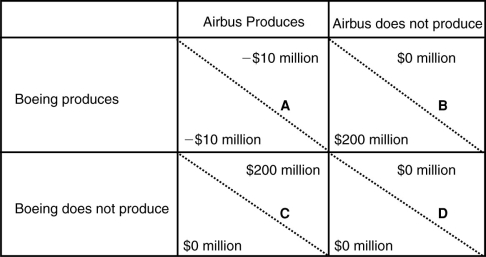 Now suppose that the U.S. government decides to provide a $50 million subsidy to Boeing to encourage it to produce superjumbo jets. Boeing decides to take the subsidy. Using the payoff matrix, what is Airbus's best strategy?
Now suppose that the U.S. government decides to provide a $50 million subsidy to Boeing to encourage it to produce superjumbo jets. Boeing decides to take the subsidy. Using the payoff matrix, what is Airbus's best strategy?
Definitions:
Government Regulation
Rules and guidelines established by the government aimed at influencing or controlling certain activities within the society or economy.
Total Surplus
The total net gain to society from a market transaction, which is the combination of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
Consumer Surplus
The gap between the aggregate amount buyers are willing and able to spend for a good or service, versus what they actually spend.
Property Rights
The legally guaranteed rights to own, use, and dispose of assets, including physical and intellectual property.
Q1: An emerging economy as a current GDP
Q18: The flow of capital investment from emerging
Q23: Uncovered interest parity refers to:<br>A) borrowing in
Q42: In what way does the high U.S.
Q51: Which of the following is an example
Q65: According to the article "A Sea Change
Q71: Which of the following countries had the
Q96: The United States and China can produce
Q141: If an emerging market economy has a
Q153: Suppose that the world price of sugar