Solve the linear programming problem by the method of corners. Maximize 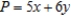 subject to
subject to 
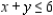
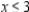
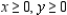
Definitions:
Cognitive Psychology
A branch of psychology that studies mental processes including how people think, perceive, remember, and learn.
Natural Drive
Intrinsic motivations or biological imperatives that guide behavior, such as hunger, thirst, or the drive for survival.
Carl Rogers
A pioneering psychologist known for developing client-centered therapy and emphasizing the importance of the self and unconditional positive regard.
Superiority
A belief in or perception of being better or more important than others.
Q21: A division of the Winston Furniture Company
Q44: Solve the system of linear equations using
Q53: Determine graphically the solution set for the
Q57: Find an equation of the circle that
Q68: National Business Machines manufactures two models of
Q75: Which point has a negative x-coordinate and
Q111: Write a system of linear inequalities that
Q164: Indicate whether the matrix is in row-reduced
Q165: The Flemings secured a bank loan of
Q288: Given that the augmented matrix in row-reduced