Solve the linear programming problem by the method of corners. Maximize 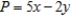 subject to
subject to 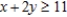
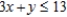
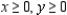
Definitions:
Allowance Method
An accounting technique that estimates and sets aside a portion of accounts receivable deemed uncollectible as an allowance for doubtful accounts.
Account Receivable
Money owed to a business by its customers for goods or services that have been delivered but not yet paid for.
Total Current Assets
The sum of all assets expected to be converted into cash, sold, or consumed within one year or the normal operating cycle, whichever is longer.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
A contra-asset account used to estimate the portion of a company's accounts receivable that may not be collectible.
Q11: Weaver and Kline, a stock brokerage firm,
Q40: A company manufactures products A, B, and
Q43: Find the accumulated amount A if the
Q50: If a merchant deposits $500 annually at
Q87: Find the book value of office equipment
Q110: Find the graphical solution of the inequality.
Q187: Consider the production problem: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6027/.jpg" alt="Consider
Q188: In how many ways can a member
Q195: Custom Office Furniture Company is introducing a
Q242: Determine whether the lines through the pair