You are given a linear programming problem. Use the method of corners to solve the problem.
Minimize 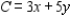
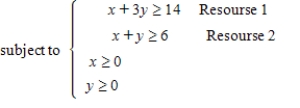
 = __________
= __________  = __________
= __________  = __________
= __________
Find the range of values that the coefficient of  can assume without changing the optimal solution.
can assume without changing the optimal solution.
≤ c ≤
Find the range of values that requirement 1 can assume.
≤ b ≤
Find the shadow price for requirement 1. Enter your answer to two decimal places, if necessary.
$ __________
Identify the binding and nonbinding constraints.
Constraint 1 is __________
Constraint 2 is __________
Definitions:
Intersectionality
A framework for understanding how aspects of a person's social and political identities (gender, race, class, sexuality, ability, etc.) combine to create different modes of discrimination and privilege.
Mary Calkins
An influential American psychologist and philosopher, notable for being the first woman to serve as president of the American Psychological Association.
U.S. Psychology
The study, practice, and application of psychological principles within the context of the United States, influenced by the country's culture, legislation, and historical events.
Conservatism
A political and social philosophy promoting traditional institutions and practices, emphasizing stability and continuity.
Q5: Determine whether the statement is true or
Q8: Determine whether the equation defines y as
Q46: Use the simplex method for solving nonstandard
Q62: For the geometric progression, find the sixth
Q101: K & R builders build three models
Q134: Ashley has earmarked at most $270,000 for
Q173: Find an equation of the line that
Q202: Determine whether the system of linear equations
Q208: Find <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6027/.jpg" alt="Find and
Q239: Determine whether the statement is true or