Solve the linear programming problem by the method of corners. Minimize 
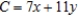 subject to
subject to 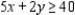
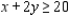
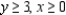
Definitions:
Congruency
The degree of alignment or agreement between two or more elements, such as organizational goals and employee behavior or values.
Client Contacts
Interactions or communications between a business and its clients, often critical for developing and maintaining relationships.
Reward Problems
Issues or challenges that arise in the process of recognizing or compensating employees' efforts and achievements.
Distributive Justice
The perceived fairness of the distribution of resources and rewards within an organization or society, influencing individuals' satisfaction and motivation.
Q24: Solve the linear programming problem by the
Q56: Formulate but do not solve the problem.<br><br>The
Q67: Solve the system of linear equations using
Q88: Use the technique developed in this section
Q91: Find the present value of an ordinary
Q113: Solve the linear programming problem by the
Q115: You are given a linear programming problem.
Q144: You are given a linear programming problem.
Q188: Formulate but do not solve the problem.
Q202: A city has $2.8 million worth of