Solve the linear programming problem by the method of corners. Minimize 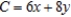 subject to
subject to 
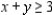
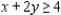
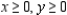
Definitions:
Beers
Alcoholic beverages made from fermented grains, primarily barley, and flavored with hops and other ingredients.
Indeterminate
A situation or outcome that is not clearly defined or decided, often because of complex or uncertain variables.
Marginal Utility
The additional satisfaction or utility that one receives from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
Donut
A fried dough confection or dessert food, usually ring-shaped or without a hole and filled with various sweet fillings or toppings.
Q46: Formulate but do not solve the following
Q82: Determine graphically the solution set for the
Q88: Formulate but do not solve the problem.
Q105: The annual interest on Sid Carrington's three
Q107: Determine graphically the solution set for the
Q114: Suppose payments will be made for <img
Q131: If Jackson deposited $400 at the end
Q166: You are given a linear programming problem.
Q175: Find the periodic payment R required to
Q189: Solve the system of linear equations using