a.complements since the coefficient on M is positive.
b.substitutes since the coefficient on M is positive.
c.complements since the coefficient on 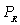 is positive.
is positive.
d.substitutes since the coefficient on 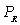 is positive.
is positive.
-The estimated demand for a good is 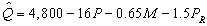 where Q is the quantity demanded of the good,P is the price of the good,M is income,and
where Q is the quantity demanded of the good,P is the price of the good,M is income,and 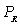 is the price of related good R.The good is
is the price of related good R.The good is
Definitions:
Product Variety
Refers to the assortment of different goods and services that a company offers to meet consumer demands.
Underallocation of Resources
A situation where resources are not being used efficiently or optimally, resulting in missed opportunities for economic or social benefits.
Monopolistic Competition
A market structure in which many companies sell products or services that are similar but not identical, allowing for some degree of market power.
Profit-maximizing
The approach by which an organization figures out the best pricing and output quantity for the highest profit.
Q2: A politician,who wants to receive the maximum
Q12: game theory,a dominant strategy is<br>A)a strategy used
Q15: Economic profit is the difference between<br>A)total revenue
Q23: Use the figure below to calculate the
Q25: The managers of Alpha and Beta must
Q51: estimating a short-run production function of the
Q57: Refer to the following figure.At a price
Q62: Use the following demand and supply functions:
Q63: In a competitive industry the market-determined price
Q109: a monopolistically competitive market,<br>A)firms are small relative