What is the EMV for Option 1 in the following decision table? 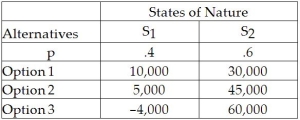
Definitions:
Inverse Demand Curve
A graphical representation showing the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity of the good that consumers are willing to purchase, plotted with price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis.
Marginal Costs
The growth in total expenditure associated with the creation of one more unit of a good or service.
Perfect Price Discrimination
A pricing strategy where a seller charges the maximum possible price for each unit consumed that the buyer is willing to pay, thus capturing the entire consumer surplus.
Total Profits
The entirety of earnings a company or individual makes after subtracting the total costs from the total revenues.
Q6: Linear programming is an appropriate problem-solving technique
Q59: Which of the following correctly describes all
Q60: The expected value of perfect information is
Q61: Product-oriented layouts tend to have high levels
Q65: In a minimization problem,a negative improvement index
Q67: The _ is the simplest approach to
Q78: A transportation problem has 8 origins and
Q81: Flexibility can be achieved with<br>A)movable equipment.<br>B)inexpensive equipment.<br>C)sophisticated
Q97: A(n)_ is an occurrence or situation over
Q133: What is the waiting-line problem? Why is