Calculate the equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 25 °C, 2 IO3-(aq) + 5 Hg( 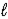 ) + 12 H+(aq) → I2(s) + 5 Hg2+(aq) + 6 H2O(
) + 12 H+(aq) → I2(s) + 5 Hg2+(aq) + 6 H2O( 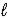 )
)
The standard reduction potentials are as follows:
IO3-(aq) + 6 H+(aq) + 5 e- → I2(s) + 3 H2O( 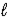 )
)
E° = +1.20 V
Hg2+(aq) + 2 e- → Hg( 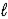 )
)
E° = +0.86 V
Definitions:
Sensory Elements
Components or factors that engage the five senses (sight, smell, sound, taste, and touch), used in various designs and experiences to enhance perception and interaction.
Scrambled Merchandising
A retail strategy where a store sells products unrelated to its primary line of business, broadening its appeal to customers.
Cross-merchandising
A retail strategy that involves displaying or suggesting complementary products from different categories to encourage additional purchases.
Complementary Merchandising
A retail strategy that involves the sale of products or services that complement each other, aimed at increasing customer satisfaction and sales.
Q5: A 2.5 L flask is filled with
Q14: Amino acids polymerize in condensation reactions that
Q16: Below is a list of complex ions
Q19: Which of the following functional groups are
Q20: What is the molecular formula for heptane?<br>A)
Q32: What mass of ethylene glycol,when mixed with
Q58: If the reaction quotient,Q,is greater than K
Q61: Which of the following ionic compounds does
Q70: Most copper minerals are mined as _.<br>A)
Q129: Which of the following elements has a