What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction, HCO2H(aq) + CN-(aq) 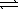 HCO2-(aq) + HCN(aq)
HCO2-(aq) + HCN(aq)
And does the reaction favor the formation of reactants or products? The acid dissociation constant,Ka,for HCO2H is 1.8 × 10-4 and the acid dissociation constant for HCN is 4.0 × 10-10.
Definitions:
Endocrine System
The endocrine system is a network of glands in the body that produces and secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate bodily functions.
Pituitary Gland
A pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain, often termed the "master gland," because it controls various hormonal functions of other endocrine glands.
Absolute Refractory Period
The period immediately following an action potential during which a neuron is incapable of firing another action potential, no matter how strong the stimulus.
Neural Impulses
Neural impulses, also known as action potentials, are the electrical signals that travel along neurons, transmitting messages throughout the nervous system.
Q26: A 10.0 g sample of solid NH<sub>4</sub>Cl
Q33: Which of the following is the largest
Q42: Write a balanced chemical equation for the
Q48: Calculate the standard reduction potential for the
Q49: What is the hydronium-ion concentration of a
Q53: A 25.0 mL sample of 0.10 M
Q57: _ is a measure of the degree
Q63: At 50°C the autoionization constant for pure
Q64: At 25 °C,0.138 mg AgBr dissolves in
Q74: Consider the following equilibrium. PCl<sub>3</sub>(g)+ Cl<sub>2</sub>(g) <img