TABLE 14-6
One of the most common questions of prospective house buyers pertains to the average cost of heating in dollars (Y) . To provide its customers with information on that matter, a large real estate firm used the following 4 variables to predict heating costs: the daily minimum outside temperature in degrees of Fahrenheit (X1) , the amount of insulation in inches (X2) , the number of windows in the house (X3) , and the age of the furnace in years (X4) . Given below are the EXCEL outputs of two regression models.
Model 1
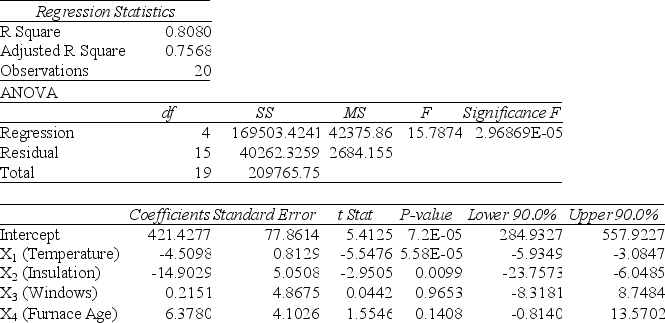 Note: 2.96869E-05 = 2.96869×10-5
Note: 2.96869E-05 = 2.96869×10-5
Model 2
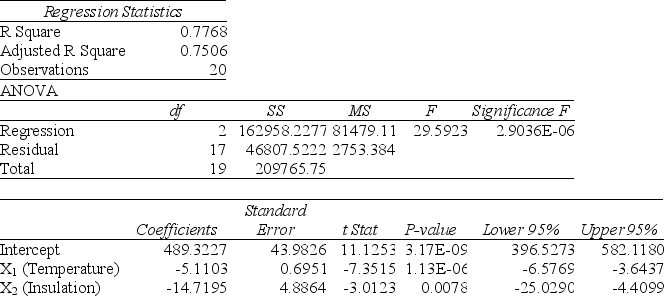 Note: 2.9036E-06 = 2.9036×10-6
Note: 2.9036E-06 = 2.9036×10-6
-Referring to Table 14-6 and allowing for a 1% probability of committing a type I error, what is the decision and conclusion for the test H0 : β1 = β2 = β3 = β4 = 0 vs. H1 : At least one βj ≠ 0, j = 1, 2, ..., 4 using Model 1?
Definitions:
Skimming Pricing
A pricing strategy where a new product is priced high initially to maximize profits from customers willing to pay more, before lowering the price over time.
Similar Goods
Similar goods are products that satisfy the same customer needs or desires and are often considered by consumers as interchangeable with each other.
Gradually Lowering
The process of slowly decreasing or reducing something over time.
Competitive Pricing
A pricing strategy where a company sets its product or service prices based on the prices of competitors, aiming to provide more value to customers.
Q28: Referring to Table 14-15, which of the
Q35: In multiple regression, the _ procedure permits
Q75: Referring to Table 13-9, the degrees of
Q81: Referring to Table 15-5, the 0 to
Q81: Referring to Table 14-1, for these data,
Q99: Referring to Table 13-3, the coefficient of
Q133: Referring to Table 12-11, suppose we want
Q150: Referring to Table 12-12, the critical value
Q175: Referring to Table 14-11, in terms of
Q178: Consider a regression in which b<sub>2</sub> =