Use the standard reaction enthalpies given below to determine 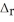 H° for the following reaction: 4SO3(g) → 4S(s) + 6O2(g)
H° for the following reaction: 4SO3(g) → 4S(s) + 6O2(g)  H° = ?
H° = ?
Given:
SO2(g) → S(s) + O2(g) 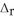 H° = +296.8 kJ
H° = +296.8 kJ
2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g) 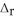 H° = -197.8 kJ
H° = -197.8 kJ
Definitions:
DIMM
Dual In-line Memory Module, a series of random-access memory modules that provide a computer's processor with the temporary data storage it needs to operate.
Physical RAM
Refers to the actual hardware memory modules installed in a computer used to temporarily store data for quick access by the processor.
Memory Storage
Devices or media used to store digital data, such as SSDs, HDDs, and memory cards.
Registered Memory
Memory modules that have extra chips (registers) near the bottom of the module that delay all data transfers by one clock tick to ensure accuracy.
Q4: The f orbital can hold a maximum
Q26: Using Lewis structures and formal charge, which
Q49: Using the following equation for the combustion
Q103: energy associated with the temperature of an
Q117: Ca-O<br>A)strongest covalent bond<br>B)longest covalent bond<br>C)weakest ionic bond<br>D)metallic
Q123: Why do atoms only emit certain wavelengths
Q150: Identify the number of valence electrons for
Q162: Calculate the frequency of light associated with
Q226: Lead ions can be precipitated from aqueous
Q259: What are the required coefficients to properly