Use the 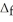 H° and
H° and 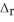 H° information provided to calculate
H° information provided to calculate 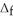 H° for SO3(g) :
H° for SO3(g) : 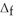 H° (kJ
H° (kJ 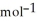 ) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g)
) 2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g) 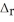 H° = -198 kJ SO2(g) -297
H° = -198 kJ SO2(g) -297
Definitions:
Binge Drinking
The consumption of an excessive amount of alcohol in a short period, typically defined as five or more drinks for men and four or more for women within about two hours.
Statistical Probability
The likelihood or chance of an event occurring, based on a scale from 0 to 1, where 0 indicates impossibility and 1 indicates certainty.
Level of Significance
A statistical measure that determines the threshold at which the null hypothesis is rejected, often denoted by alpha (α).
Null Hypothesis
A statistical presumption positing that there is no notable difference or impact.
Q2: What is the general valence-electron ground-state electron
Q23: The d orbital can hold a maximum
Q103: Place the following types of electromagnetic radiation
Q128: Identify the compound with (an) ionic bond(s).<br>A)
Q140: Two samples of calcium fluoride are decomposed
Q163: Which of the following quantum numbers describes
Q171: Automotive air bags inflate when sodium azide
Q217: Why is sugar water not a good
Q226: Lead ions can be precipitated from aqueous
Q244: If 100. mL of 0.400 mol L<sup>-1</sup>