Use the standard reaction enthalpies given below to determine 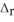 H° for the following reaction: 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
H° for the following reaction: 2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g) 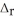 H° = ?
H° = ?
Given:
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g) 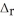 H° = +183 kJ
H° = +183 kJ
1/2 N2(g) + O2(g) → NO2(g) 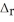 H° = +33 kJ
H° = +33 kJ
Definitions:
RR Parent
Refers to a plant that is homozygous for the round seed shape allele in Mendelian genetics, "RR" signifies both alleles for a trait are the same (dominant).
Dominant Phenotype
The observable trait or characteristics of an organism that masks the effect of a recessive allele; it is expressed in the phenotype when a dominant allele is present.
Genotype
The genetic constitution of an individual organism, determining specific traits by its DNA sequence.
Aa
An abbreviation often used in genetics to denote a homozygous recessive genotype.
Q12: When 31.2 mL of 0.500 mol L<sup>-1</sup>
Q44: Which of the following compounds is an
Q47: How can you tell if a reaction
Q48: Balance the chemical equation given below, and
Q48: The standard state of sulfur is _.
Q49: How many grams of H<sub>3</sub>PO<sub>4</sub> are in
Q75: How many grams of calcium chloride are
Q84: Place the following gases in order of
Q164: Only two electrons, with opposing spins, are
Q259: What are the required coefficients to properly