Three nonequivalent Lewis structures for carbonyl sulfide, SCO, are given below. Use the concepts of formal charge and electronegativity to choose the structure that is the best representation. 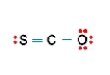 A
A 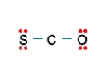 B
B 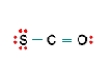 C
C
Definitions:
Stimulus-Response Connections
The association between a specific stimulus and a particular response, fundamental to classical and operant conditioning theories.
Information Processing
The method by which individuals intake, analyze, store, and retrieve information, drawing parallels to computer processing.
Drives
Biological needs that motivate an organism to fulfill them, such as hunger, thirst, or the need for warmth.
Genetic Variability
The diversity in gene frequencies within a population, leading to differences in traits and potentially in susceptibility to diseases.
Q2: Determine the enthalpy change for the
Q7: Lithium has two naturally occurring isotopes, <sup>6</sup>Li
Q17: In a reaction coordinate diagram, reacting molecules
Q17: You have 2.50 g of each of
Q31: Which anion will form a precipitate with
Q41: In the NO<sub>2</sub><sup>-</sup> ion, each atom can
Q43: _ is a measure of the degree
Q50: Which of the following groups is a
Q71: The pressure exerted by gas molecules inside
Q92: Which of the following sets of ions