In the manufacture of vitamin capsules, the proportion of calcium in each capsule has a specification of 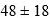 parts per million (ppm). A random sample of 100 capsules revealed a sample average calcium content of 44.5 ppm and a sample standard deviation of 3.2 ppm. Management uses
parts per million (ppm). A random sample of 100 capsules revealed a sample average calcium content of 44.5 ppm and a sample standard deviation of 3.2 ppm. Management uses 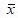 and R-charts to monitor the calcium amount using samples of size 4. The charts depict an in-control process.
and R-charts to monitor the calcium amount using samples of size 4. The charts depict an in-control process.
The centerline of the R chart is 6.7 and the centerline of the 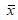 chart is 44.8.
chart is 44.8.
a Compute 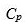 for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard
for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard
deviation derived from the random sample.
b. Compute 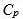 for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard
for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard
deviation derived from the control chart parameters.
c. Compute 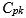 for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard
for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard
deviation derived from the random sample.
. Compute 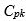 for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard
for this process using estimates of the process mean and standard
deviation derived from the control chart parameters
d. What do the differences between the values of 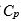 and
and 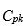 tell you?
tell you?
Definitions:
Continental Collision
The process whereby two continental plates collide, leading to mountain building and seismic activity.
Subduction
The process by which one tectonic plate moves beneath another plate and sinks into the mantle due to gravitational forces.
Conduction
The process by which heat or electricity is directly transmitted through a substance when there is a difference of temperature or electrical potential.
Subduction Zone
A region where one tectonic plate moves under another, leading to volcanic activity and earthquakes.
Q1: A manager at a local manufacturing company
Q3: Which of the following practices will lead
Q24: In K&N's process management framework,which of the
Q24: _ is the process of designing a
Q32: A confidence interval is an interval estimate
Q35: As per the model that describes the
Q48: In the context of the dimensions of
Q54: In the manufacture of vitamin capsules, the
Q61: The distance from the target to the
Q72: x-charts are used for:<br>A)averages of variables data.<br>B)individual