A real (non-Carnot) heat engine, operating between heat reservoirs at temperatures of 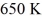 and
and 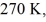 performs 4.3 kJ of net work and rejects
performs 4.3 kJ of net work and rejects 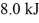 of heat in a single cycle. The thermal efficiency of this heat engine is closest to
of heat in a single cycle. The thermal efficiency of this heat engine is closest to
Definitions:
Peripheral Chemoreceptors
Sensory receptors located in the carotid and aortic bodies that detect changes in the chemical composition of blood, including oxygen and carbon dioxide levels.
Oxygen Levels
The concentration of oxygen in a particular environment, often measured in terms of partial pressure or saturation.
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure is the force exerted by circulating blood on the walls of the body's arteries, important for maintaining blood flow through the body.
Pulmonary Circulations
The part of the circulatory system specifically responsible for carrying deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs and returning oxygenated blood back to the heart.
Q2: The figure shows two tiny 5.0-g spheres
Q12: What is the change in entropy of
Q23: The figure shows four Gaussian surfaces surrounding
Q24: A brass rod is 40.1 cm long
Q24: A cylindrical wire of radius 2.0 mm
Q29: A thin, circular disk of radius 30.0
Q31: Two large conducting parallel plates A and
Q34: In a transformer, how many turns are
Q36: A charged particle of mass 0.0020 kg
Q46: The interior of a refrigerator has a