The solution to the inequality 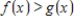 occurs where the graph of
occurs where the graph of 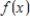 lies above the graph of
lies above the graph of 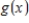 .
.
Definitions:
Regressive Tax
At the individual level, a tax whose average tax rate decreases as the taxpayer’s income increases. At the national level, a tax for which the average tax rate (= tax revenue/GDP) falls as GDP rises.
Income Groups
Categories of individuals or households segmented by income levels, often used for statistical analysis and policy design.
Proportional Tax
At the individual level, a tax whose average tax rate remains constant as the taxpayer’s income increases or decreases. At the national level, a tax for which the average tax rate (= tax revenue/GDP) remains constant as GDP rises or falls.
Benefits-received Principle
The concept that the amount of taxes an individual pays should be directly proportional to the level of benefits or services they receive from the government.
Q14: An initial investment of $545.45 declines at
Q18: The inverse of a logarithm is an
Q20: The concentration D of a drug, in
Q25: A pipeline is to span a horizontal
Q25: Piecewise-defined functions occur in such applications as
Q32: For a satellite orbiting Earth, the time
Q33: Make the graph of <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7296/.jpg" alt="Make
Q40: Researchers have developed a "bionic arm." This
Q41: For the power function <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7296/.jpg" alt="For
Q133: A stroke is also known as a