Use the paragraph and accompanying figure to answer the following questions.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects cells that have both CD4 and CCR5 cell surface molecules. The viral nucleic acid molecules are enclosed in a protein capsid, and the protein capsid is itself contained inside an envelope consisting of a lipid bilayer membrane and viral glycoproteins. One hypothesis for viral entry into cells is that binding of HIV membrane glycoproteins to CD4 and CCR5 initiates fusion of the HIV membrane with the plasma membrane, releasing the viral capsid into the cytoplasm. An alternative hypothesis is that HIV gains entry into the cell via receptor-mediated endocytosis, and membrane fusion occurs in the endocytotic vesicle. To test these alternative hypotheses for HIV entry, researchers labeled the lipids on the HIV membrane with a red fluorescent dye.
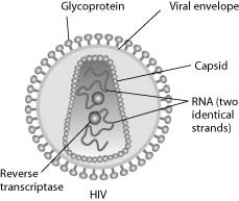
-What would be observed by live-cell fluorescence microscopy immediately after HIV entry if HIV is endocytosed first, and then later fuses with the endocytotic vesicle membrane?
Definitions:
Consumer Goods
Products and services that are consumed by individuals or households to satisfy their needs or wants.
Producing
The process of creating, manufacturing, or constructing goods and services for consumption or use.
Economic Growth
An increase in the production of goods and services in an economy over a period, indicating improving national prosperity.
Production Possibilities Frontier
A curve depicting all maximum output possibilities for two goods, given a set of inputs resources and technology.
Q3: Both the volume and the surface area
Q6: Which of the following is not a
Q10: What was the most significant conclusion that
Q16: In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red
Q17: Feather color in budgies is determined by
Q24: Use the figures to answer the question.<br><img
Q27: Which of the following molecules is most
Q56: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1096/.jpg" alt=" Based on Figure
Q57: Three lab groups carried out an experiment
Q62: In which reactions of cellular respiration and