Use the following information to answer the question.
Canadian and Swiss researchers wanted to know if the diversity of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF) was important to the productivity of grasslands (M.G.A. van der Heijden, J. N. Klironomos, M. Ursic, P. Moutoglis, R. Streitwolf-Engel, T. Boler, A. Wiemken, and I. R. Sanders. 1998. Mycorrhizal fungal diversity determines plant biodiversity, ecosystem variability, and productivity. Nature 396:69-72) . Specifically, they wanted to know if it mattered which specific AMF species were present, or just that some type of AMF was present. They grew various plants in combination with one of four AMF species (A, B, C, and D) , no AMF species (O) , or all four AMF species together (A + B + C + D) ; and they measured plant growth under each set of conditions. All plant species were grown in each plot, so they always competed with each other with the only difference being which AMF species were present.
On the graphs, the x-axis labels indicate the number and identity of AMF species (bar 0 = no fungi; bars A - D = individual AMF species; bar A + B + C + D = all AMF species together) . The y-axis indicates the amount (grams) of plant biomass for the species shown in italics above each graph. Graph e is the total biomass (grams) of all 11 plant species combined; graph f is the biomass of Bromus erectus plants only, separated from the total.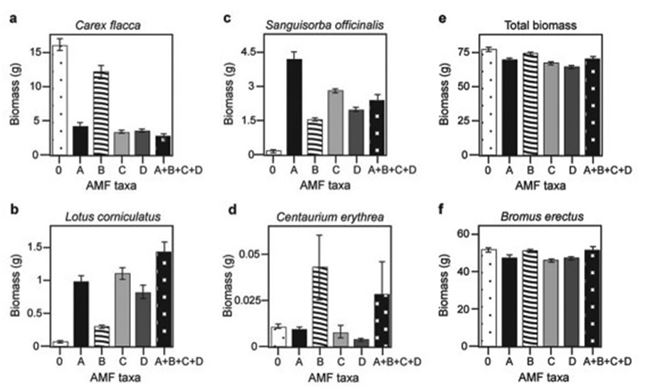
What is the major difference between Bromus erectus (graph f) and the other plant species (graphs a-d) included in the study?
Definitions:
Tactile Stimulation
The use of touch to stimulate the sensory system, often employed in therapeutic contexts to encourage mental and physical growth or to induce relaxation.
Birth Weight
The weight of a newborn measured immediately after birth.
Visual Stimulation
Exposure to visual cues that promote sensory processing and cognitive development, especially significant in early childhood development.
Peek-a-boo
A common game played with young children, involving hiding and revealing one's face to surprise the child.
Q17: Which of the following would be least
Q19: Sexual reproduction in eukaryotes increases genetic variation.
Q20: What is the most accurate method used
Q26: Use the information to answer the following
Q34: Which one of the following does not
Q39: Use the following information to answer the
Q50: Use the following information and figures to
Q55: Similar to most amoebozoans, the forams and
Q71: A botanist discovers a new species of
Q73: Which of the following sex and generation