Exhibit 12.2
The following questions use the information below.
The owner of Fix-a-dent Auto Repair wants to study the growth of his business using simulation. He is interested in simulating the number of damaged cars and the amount of damage to the cars each month. He currently repairs 100 cars per month and feels the change in number of cars can vary uniformly between a decrease of as much as 3% and an increase of up to 5% (average change of 1%) . The dollar value of the damage to the cars is a normally distributed random variable with a mean of $3,000 and a standard deviation of $500. The average repair bill has been increasing steadily over the years and the owner expects the mean repair bill will increase by 1% per month. A spreadsheet model to simulate the problem has been run 300 times. A part of the simulation statistics output from Risk Solver Platform (RSP) and a spreadsheet for computing confidence intervals follows. 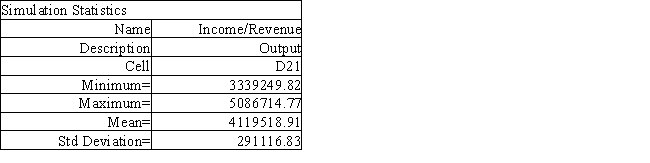
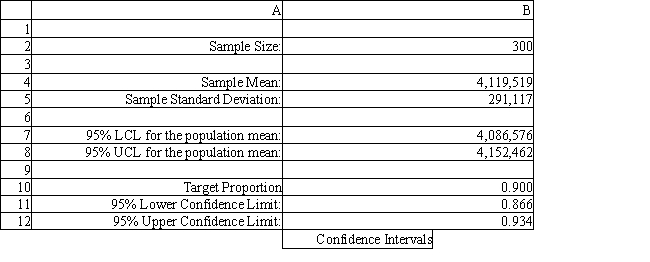
-Using the information in Exhibit 12.2, what formula should go in cell B8 of the Confidence Intervals spreadsheet to compute the upper limit on a 95% confidence interval for the true population mean?
Definitions:
Coercive Power
The ability to control others through the threat of punishment or the imposition of unpleasant conditions.
Legitimate Power
Power that is recognized and accepted by others within an organizational hierarchy due to a person's position or authority.
Valet Manager
A person responsible for overseeing the operation of parking services and managing valet staff.
Logical Power
Logical power, often related to the concept of rational-legal authority, depends on an individual's ability to use logic and reason to persuade or influence others.
Q5: A small town wants to build
Q7: In the Delphi method, the opinions of
Q23: A constraint which cannot be violated is
Q24: A company wants to use PERT to
Q32: In the equation L<sub>S</sub> = L<sub>Q </sub>+
Q36: Refer to Exhibit 8.2. What values would
Q39: What are the immediate successors of activity
Q46: Planning for service capacity involves prediction of
Q47: Which type of queuing system are you
Q56: The GRG and Simplex algorithms are similar