Exhibit 15.1
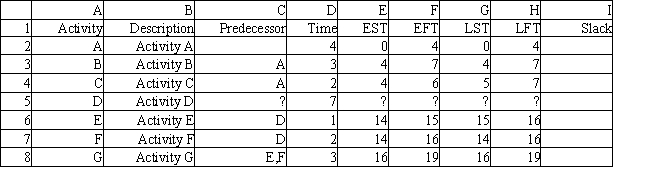
The following questions employ the AON network and partial spreadsheet below. 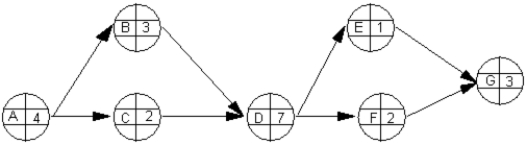
-Activity-on-Arc (AOA) networks do not allow multiple arcs with common start and finish nodes. If this must be represented, how is an AOA network modified?
Definitions:
Critical Paths
The sequence of stages determining the minimum time needed to complete a project, where any delay in the critical path tasks will directly affect the project completion date.
Critical Path
The longest sequence of activities in a project plan which must be completed on time for the project to finish by its due date.
Immediate Predecessor
Refers to an immediately preceding task or step that must be concluded before the next one can start, in a sequence of operations or processes.
Q2: In the decision to locate a public
Q12: Costs for preparing time-series forecasts generally are
Q24: Refer to Exhibit 11.10. What Excel command
Q28: Refer to Exhibit 13.3. What is the
Q33: Mayo Clinic is a service firm that
Q34: Every nonprobabilistic method has a weakness for
Q36: Using the information in Exhibit 12.2, what
Q56: Refer to Exhibit 10.7. What formulas should
Q71: A grocery clerk can serve 20 customers
Q89: A "risk averse" decision maker assigns the