TABLE 13- 11
A company that has the distribution rights to home video sales of previously released movies would like to use the box office gross (in millions of dollars) to estimate the number of units (in thousands of units) that it can expect to sell. Following is the output from a simple linear regression along with the residual plot and normal probability plot obtained from a data set of 30 different movie titles:
ANOVA
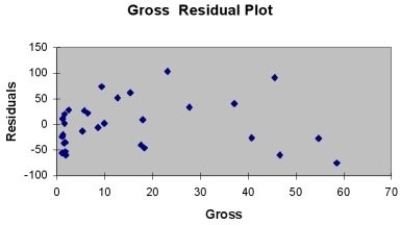
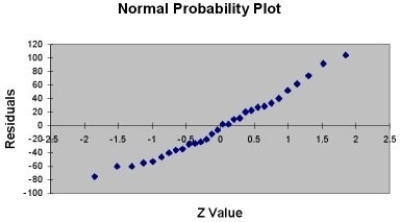
-Referring to Table 13-11, there is sufficient evidence that box office gross and home video unit sales are linearly related at a 5% level of significance.
Definitions:
Net Operating Income
A measure of a company's profitability from its core business operations, excluding taxes and interest expenses.
Direct Labor Cost
The total cost of workforce directly involved in the production of goods or services, excluding indirect labor such as administration.
Variable Costing
A costing technique that only assigns variable production costs to inventory, helping managers understand the impact of production levels on total costs.
Net Operating Income
The income produced through a firm's regular commercial activities, not including taxes and interest.
Q13: Referring to Table 15-8, the quadratic effect
Q24: Referring to Table 14-4, what is the
Q39: One of the consequences of collinearity in
Q49: Referring to Table 11-5, what degrees of
Q66: Referring to Table 14-16, there is sufficient
Q95: Referring to Table 14-11, which of the
Q109: Referring to Table 14-4, what is the
Q113: Referring to Table 13-10, what are the
Q152: Referring to Table 13-2, to test that
Q158: Referring to Table 11-9, the critical value