Vista Corporation, producer of computer software packages, began operations on January 1. It acquired financing from the issuance of common stock for $60,000,000 and long-term debt for $80,000,000. At the beginning of business operations, Vista produced the following projected income statement and balance sheet for the first year. All amounts are in thousands.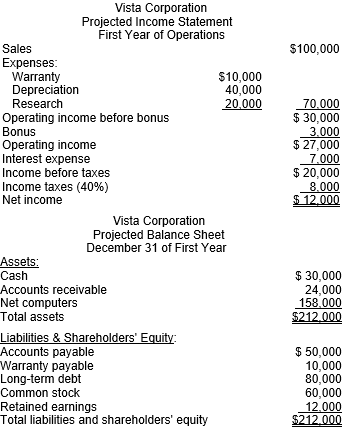
The new president is rather disappointed with these projected results having just quit a job of which his compensation package was $4,000,000. After examining the forecasts of a bonus of only $3,000,000, the president decides to use his knowledge of financial statements to modify his bonus. He meets with the company's CFO the next day to see what could be done. He suggested the following possibilities that would boost the first year's income:
1. Slash research and development expenditures, which are paid in cash, from $20 million to $10 million.
2. Double the estimated life of the computers, which will decrease depreciation expense from $40 million to $20 million. Because identical accounting procedures are used for taxes, no deferred taxes will be generated. Taxes require immediate payment.
3. Reduce estimated warranty expense from 10% of sales to 7% of sales.
4. Any resultant change in the bonus of 10% of operating income before the bonus will be paid to the president in cash.
A. Adjacent to the income statement for Year 1, create a new statement using the alternative accounting procedures and operating decisions.
B. Compare the president’s compensation if the changes in part A are enacted with his current compensation. What are the ramifications of these changes on the future?
Definitions:
Full Cost
The total cost of production that includes direct and indirect costs, such as raw materials, labor, and overhead expenses.
Mark-Up Percentage
A pricing strategy that sets the selling price of a product by adding a specific percentage to its cost price.
Cost-Plus Pricing
A pricing strategy where the selling price is determined by adding a specific markup to a product's cost, ensuring all costs are covered and a profit is guaranteed.
Absorption Cost
A method of product costing that includes all manufacturing costs - direct materials, direct labor, and both variable and fixed overhead.
Q21: The following information was taken from
Q45: A call provision in a bond contract
Q58: What two criteria must be met for
Q68: Passive investments in equity securities are:<br>A)readily marketable
Q79: All of the following are typically associated
Q98: What concerns might exist when a company's
Q99: On November 30, 2017, Arnold Company purchased
Q104: Ruby uses the LIFO cost flow assumption.
Q110: On January 1, 2016 Frank Corporation issued
Q115: On December 31, 2016, Creative Corporation issued