Suppose that Ms. Smart invests 25% of her portfolio in four different stocks. The mean and standard deviation of the annual return on each stock are shown in the first table below. The correlations between the annual returns on the four stocks are shown in the second table below.
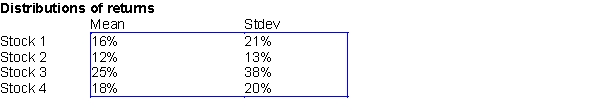
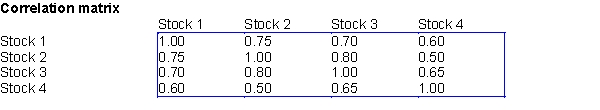
-(A) Use @RISK with 100 replications, provide a summary statistics of portfolio return; namely, minimum, maximum, mean, and standard deviation.
(B) Use your answers to (A) to estimate the probability that Mrs. Smart's portfolio's annual return will exceed 20%.
(C) Use your answers to (A) to estimate the probability that Mrs. Smart's portfolio will lose money during the course of a year.
(D) Suppose that the current price of each stock is as follows: stock 1: $16; stock 2: $18; stock 3: $20; and stock 4: $22. Ms. Smart has just bought an option involving these four stocks. If the price of stock 1, six months from now are is $18 or more, the option enables Ms. Smart to buy, if she desires, one share of each stock for $20 six months from now. Otherwise the option is worthless. For example, if the stock prices six months from now are: stock 1: $18; stock 2: $20; stock 3: $21; and stock 4: $24, then Ms. Smart would exercise her option to buy stocks 3 and 4 and receive (21- 20) + (24-20) = $5 in each cash flow. How much is this option worth if the risk-free rate is 8%?
Definitions:
Expense Account
An account used to track money spent or costs incurred in the operation of a business, helping in understanding and managing expenses.
Interest Payable
A liability account showing the amount of interest expense that has been incurred but not yet paid.
Fiscal Period
A specific time period used for accounting purposes and financial reporting, usually spanning a year, but can also be a quarter or month.
Adjusting Entry
Bookkeeping entries executed at the termination of an accounting cycle, intended to apportion income and outlays to their respective periods of occurrence.
Q3: (A) Find an optimal solution to the
Q7: Which of the variables have a negative
Q13: Which of the states listed paid their
Q27: In simple linear regression, if the error
Q29: Calculate the interquartile range. What does this
Q38: The number of people entering a shopping
Q62: The flows in a general minimum cost
Q64: If a scatterplot of residuals shows a
Q65: You will always get more accurate forecasts
Q93: Perform a simulation assuming the plant will