Suppose the cost C of removing p percent of the particulate pollution from the exhaust gases at an industrial site is given by 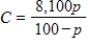 . Because p is the percent particulate pollution, we know
. Because p is the percent particulate pollution, we know  . Use the restriction on p and experiment with a C-range to obtain an accurate graph of the equation. Determine the p-intercept and explain its meaning.
. Use the restriction on p and experiment with a C-range to obtain an accurate graph of the equation. Determine the p-intercept and explain its meaning.
Definitions:
Physical Capital
Assets that are tangible, such as buildings, machinery, and equipment, which are used in the production of other goods and services.
Manufactured Resources
Goods that have been processed or created through manufacturing, used in the production of other goods or services.
Derived Demand
The demand for a factor of production resulting from the demand for the final product it helps to produce.
Factor of Production
A rephrased definition would be the essential elements required for producing goods and services, encompassing land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship.
Q8: The table below shows the national expenditures
Q20: A polynomial is an expression of form
Q65: A company manufactures two types of electric
Q87: Factor the expression completely. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1243/.jpg"
Q118: Is it true for matrices (as it
Q159: Assume that <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1243/.jpg" alt="Assume that
Q179: A manufacturer sells watches for $75 per
Q181: Evaluate the following expression. <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB1243/.jpg"
Q183: Suppose the cost C of removing p
Q295: Compute and simplify so that only positive