On January 1, 20X1, Parent Company purchased 100% of the common stock of Subsidiary Company for $390,000. On this date, Subsidiary had common stock, other paid in capital, and retained earnings of $50,000, $100,000, and $200,000 respectively. Any excess of cost over book value is due to goodwill. Parent accounts for the Investment in Subsidiary using the simple equity method.
On January 1, 20X2, Parent purchased equipment for $204,120 and immediately leased the equipment to Subsidiary on a 4-year lease. The minimum lease payments of $60,000 are to be made annually on January 1, beginning immediately, for a total of 4 payments. The implicit interest rate is 12%. The lease provides for an automatic transfer of title at the end of 4 years. The estimated useful life of the equipment is 6 years. The lease has been capitalized by both companies.
A lease amortization schedule, applicable to either company, is presented below: 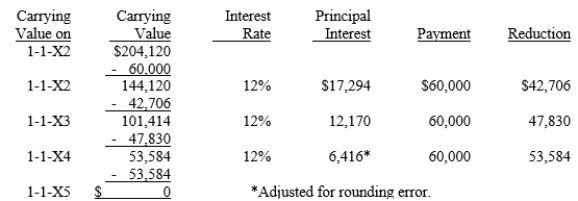
On January 1, 20X3, Parent held merchandise acquired from Subsidiary for $10,000. During 20X3, subsidiary sold merchandise to Parent for $50,000, of which $15,000 is held by Parent on December 31, 20X3. Subsidiary's usual gross profit on affiliated sales is 40%.
Required:
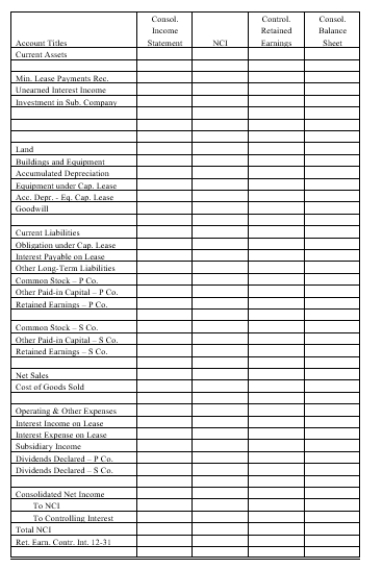
Complete the Figure 5-12 worksheet for consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 20X3. Round all computations to the nearest dollar. 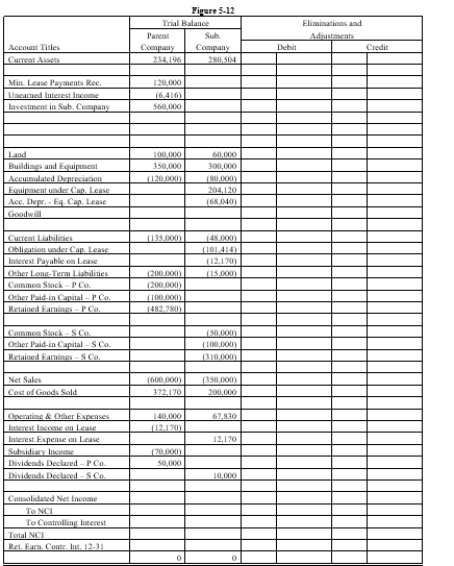
Definitions:
Defense Reaction
A psychological or physiological response to a perceived threat to one’s well-being, often involving strategies to cope with stress or anxiety.
Learned Taste Aversion
The phenomenon where an individual develops a dislike or avoidance of a particular food after a negative experience, such as sickness, that gets associated with that food.
Trial-And-Error Learning
Trial-and-error learning is a form of problem-solving that involves attempting different solutions and learning from mistakes until the correct solution is found.
Response Control
The ability to regulate one's reactions to external stimuli, often in the context of behavioral psychology.
Q7: Under the bonus method, when a new
Q9: A derivative:<br>A)requires little or no initial investment.<br>B)derives
Q18: Selected information from the separate and consolidated
Q20: Wolters Corporation is a U.S. corporation that
Q36: On January 1, 20X3, Pope Company acquired
Q42: Refer to King Cotton Company. Describe briefly
Q48: Which of the following statements regarding bonds
Q50: Which of the following statements regarding contingent
Q77: The payment of Accounts Payable results in
Q166: Refer to Georgia's Salon. On May 31,