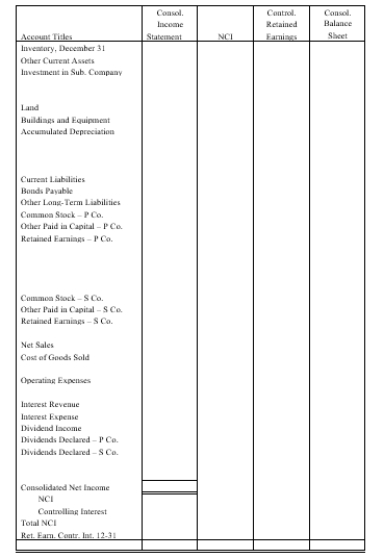
On January 1, 20X1, Powers Company acquired 80% of the common stock of Sculley Company for $195,000. On this date Sculley had total owners' equity of $200,000 (common stock, other paid-in capital, and retained earnings of $10,000, $90,000, and $100,000 respectively).
Any excess of cost over book value is attributable to inventory (worth $6,250 more than cost), to equipment (worth $12,500 more than book value), and to patents. FIFO is used for inventories. The equipment has a remaining life of five years and straight-line depreciation is used. The excess to the patents is to be amortized over 20 years.
On July 1, 20X2 Sculley borrowed $100,000 from Powers with a 10% 1-year note; interest is due at maturity.
On January 1, 20X2, Powers held merchandise acquired from Sculley for $10,000. During 20X2, Sculley sold merchandise to Powers for $50,000, $20,000 of which is still held by Powers on December 31, 20X2. Sculley's usual gross profit on affiliated sales is 50%.
On December 31, 20X1, Powers sold equipment to Sculley at a gain of $10,000. During 20X2, the equipment was used by Sculley. Depreciation is being computed using the straight-line method, a five-year life, and no salvage value.
Both companies have a calendar-year fiscal year.
Assume that during 20X1 and 20X2, Powers has appropriately accounted for its investment in Sculley using the cost method.
Required:
a.Using the information above or on the Figure 4-5 worksheet, prepare a determination and distribution of excess schedule.
b.Complete the Figure 4-5 worksheet for consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 20X2. 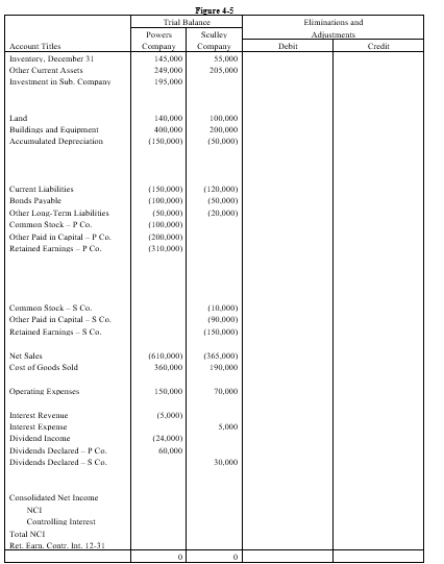
Definitions:
Contribution Format Income Statement
An income statement format that segregates fixed and variable costs, directly showing the contribution margin.
Sales Commissions
A portion of sales revenue paid to sales employees as a reward for selling the company's products or services.
Net Operating Income
Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT), representing the profit from normal business operations.
Fixed Expenses
Expenses that remain constant regardless of production or sales volumes, including items like rent, salaries, and insurance fees.
Q7: Jones company acquired Jackson Company for $2,000,000
Q8: Apple Inc. owns a 90% interest in
Q15: On January 1, July 1, and December
Q29: Rhante is a German company wholly owned
Q31: On January 1, 20X1, Prism Company purchased
Q56: In a hedge of a forecasted transaction,
Q77: Refer to King Cotton Company. Which long-term
Q118: A company's employees earn $5,000 per day,
Q122: Double-declining-balance depreciation is most commonly used by
Q131: A company issued $500,000 of bonds for