The chemical acidity of a solution is measured in units of pH: 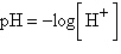 , where
, where 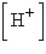 is the hydrogen ion concentration in the solution. If a sample of rain has a pH of 3.2, how many times higher is its
is the hydrogen ion concentration in the solution. If a sample of rain has a pH of 3.2, how many times higher is its 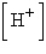 than pure water's, which has a pH of 7?
than pure water's, which has a pH of 7?
Definitions:
Faint Stimulus
A stimulus that is barely detectable or at the threshold of conscious perception.
Signal Detection Theory
A means to quantify the ability to discern between information-bearing patterns and random patterns that distract from the information.
Competing Background
Situations or environments that offer contrasting or conflicting contexts, requiring differentiation and adaptation.
Priming
A mental phenomenon in which experiencing one stimulus affects the reaction to another stimulus that follows, all happening without deliberate direction or awareness.
Q11: Find the standard form of the equation
Q17: Find the determinant of the matrix <img
Q21: Find the difference quotient and simplify your
Q36: Which of the following is unlikely to
Q41: Evaluate the logarithm <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4588/.jpg" alt="Evaluate the
Q42: Andrews Corporation buys on terms of 2/8,
Q43: From the graph of the quadratic function
Q43: Refer to Table 8-2. If capital costs
Q45: Using a graphing utility, graph <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB4588/.jpg"
Q70: A perfectly competitive firm's demand curve<br>A) has