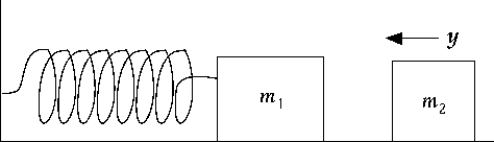
 A mass of 0.50 kg is attached to a massless spring with a spring constant k = 600 N/m see figure above) . The system rests on a level, friction-free surface and is initially at rest. A second mass of 0.20 kg makes an elastic head-on collision with the mass attached to the spring; thereafter, the oscillating system vibrates with an amplitude of 0.25 m. What was the incident speed of the second mass?
A mass of 0.50 kg is attached to a massless spring with a spring constant k = 600 N/m see figure above) . The system rests on a level, friction-free surface and is initially at rest. A second mass of 0.20 kg makes an elastic head-on collision with the mass attached to the spring; thereafter, the oscillating system vibrates with an amplitude of 0.25 m. What was the incident speed of the second mass?
Definitions:
Mathematical Models
Representations of real-world systems through mathematical concepts and language, used in a wide range of sciences to predict and analyze behaviors.
Controlled Experiments
Experimental setups in which researchers manipulate one variable while holding all other variables constant to study cause and effect relationships.
Inputs And Outputs
Refers to the materials, energy, or information that enters a system (inputs) and the results or products that come out of it (outputs).
Scientific Laws
Statements based on repeated experiments or observations that describe or predict a range of natural phenomena.
Q5: A block of material has a
Q5: In a real collision,<br>A) kinetic energy is
Q9: When a substance changes phase, from solid
Q10: Which of the following statements is one
Q22: Two particles, each of mass m, are
Q34: Two wave trains of the same frequency
Q78: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7291/.jpg" alt=" A solid cylinder
Q108: You have a rope that is 10
Q114: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7291/.jpg" alt=" The graph shows
Q158: At an outdoor bandstand, what would be