Does the gas leakage rate from automobile tires depend on the type of gas used to fill them? A sample of automobile tires are filled with nitrogen to a pressure of 1 atmosphere, and the time is measured for the internal pressure to fall to 0.9 atmospheres. The experiment is repeated for this sample of tires, but using sulfur hexafluoride in place of nitrogen. The results are summarized below. 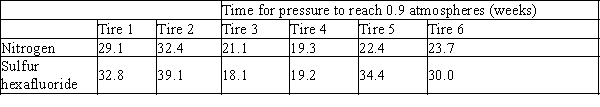 The null hypothesis is that the difference in mean population leak times is zero. Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean of population differences in leak times. Assume the leak times are normally distributed.
The null hypothesis is that the difference in mean population leak times is zero. Calculate a 95% confidence interval for the mean of population differences in leak times. Assume the leak times are normally distributed.
Definitions:
Book Sales
The commercial transaction of purchasing books from a retailer or directly from the publisher.
Cover Pictures
Visual images used on the front cover of various publications, including books, magazines, and albums, often designed to appeal to potential buyers or users.
Data
Data refers to collected facts and statistics, whether qualitative or quantitative, that can be analyzed to generate information, insights, or conclusions.
Significance Level
A threshold in hypothesis testing that defines the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is actually true, often denoted by alpha.
Q1: Inspecting meat is a very important part
Q5: Suppose you want to learn how often
Q6: When performing tests of hypotheses, there are
Q7: List the five step process that should
Q7: An outlier is an unusually small or
Q22: Profitability ratios measure a company's ability to
Q33: Identify the three types of sales taxes
Q33: When constructing a confidence interval for the
Q37: Data were collected on y = price
Q132: KPop estimates their embossing machine will last